Namma Yatri Introduction

Namma Yatri, an auto-rickshaw hailing service, has taken the Indian urban mobility sector by storm, particularly in Bengaluru. It is a homegrown ride-hailing platform that connects passengers with auto drivers directly, bypassing hefty commissions typically charged by intermediary platforms. Namma Yatri has earned a reputation for being a cost-effective, driver-friendly, and transparent service. This blog explores the success story of Namma Yatri, its business model, funding details, founders’ journey, key milestones, and its future potential.
Founder Story

Namma Yatri’s journey began with Nandan Nilekani, one of India’s most renowned tech visionaries and co-founder of Infosys. Known for his work in building large-scale digital infrastructure, such as India’s Aadhaar system, Nilekani saw an opportunity to transform the ride-hailing industry, particularly for auto-rickshaw drivers, who were often at the mercy of high commissions and fluctuating fares imposed by existing ride-hailing platforms like Uber and Ola.
Nilekani’s motivation stemmed from his belief that technology could be leveraged to create a fairer and more inclusive system for all stakeholders, particularly the auto drivers who provide essential transport services but often receive the least financial benefit. His vision was clear: to create a platform where drivers could retain full control of their earnings, without having to pay exorbitant commissions to middlemen, while ensuring that passengers could access affordable, government-regulated fares.
To bring this vision to life, Nilekani collaborated with the Beckn Foundation, a nonprofit organization focused on building decentralized digital infrastructure. The foundation developed the Beckn Protocol, an open-source platform designed to enable peer-to-peer connectivity between service providers and consumers. Unlike traditional ride-hailing apps that are centralized and charge commissions, the Beckn Protocol is designed to facilitate direct, commission-free interactions between drivers and passengers.
The Beckn Protocol is the technological backbone of Namma Yatri, making it possible for auto drivers to operate independently without being tied to a large corporate platform. Drivers can register on the app, set their availability, and accept rides, all while retaining 100% of the fare. This open-source technology empowers drivers and gives them the flexibility to work on their own terms, while passengers enjoy transparent, government-regulated pricing without the hidden costs of surge pricing or commissions.
While Nilekani provided the vision and initial support, the operational leadership came from the Beckn Foundation team. The foundation’s primary goal was to create an interoperable system that could be used across multiple cities and regions, allowing Namma Yatri to scale without the typical growing pains associated with ride-hailing services. The success of this approach lies in the foundation’s ability to build a platform that not only supports driver autonomy but also integrates seamlessly with local government regulations and unions.
Namma Yatri’s driver-first philosophy resonated strongly with auto-rickshaw unions and drivers in Bengaluru. The platform gained early traction by partnering with the Auto Rickshaw Drivers’ Union (ARDU) and other local organizations, ensuring that drivers had a voice in shaping the platform and that their needs were being prioritized. Unlike other ride-hailing services that focus on maximizing profits, Namma Yatri’s primary goal was to create a sustainable, equitable model that benefited both drivers and passengers.
Nilekani’s deep understanding of technology and his commitment to public good have been key factors in the success of Namma Yatri. His influence and vision have helped bridge the gap between technological innovation and social impact, making Namma Yatri not just a ride-hailing service but a movement aimed at redefining urban mobility. The platform’s success in Bengaluru has laid the groundwork for its potential expansion to other cities, and its open-source, community-driven model serves as a blueprint for more equitable, tech-enabled solutions in the future.
Namma Yatri Business Model: Zero Commission, Maximum Transparency
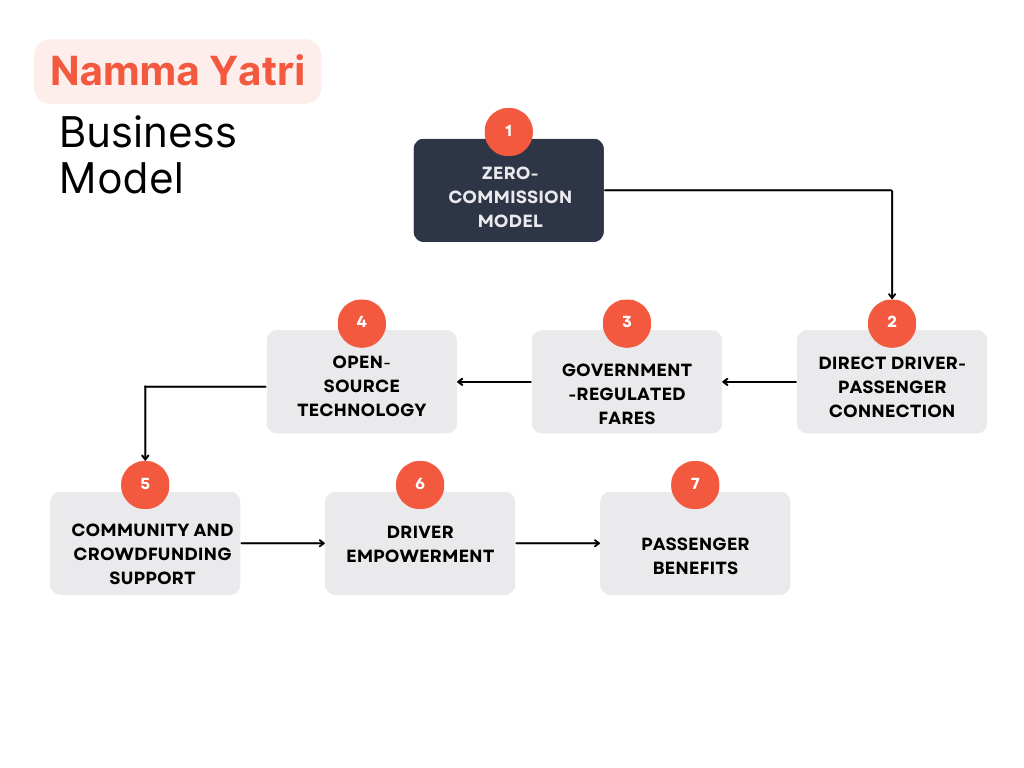
Namma Yatri operates on a unique zero-commission business model, designed to offer both passengers and drivers a better deal than conventional ride-hailing services.
Zero-Commission Model
At the core of Namma Yatri’s business model is its zero-commission policy. Unlike conventional ride-hailing platforms like Uber or Ola, which take a significant percentage of the fare as commission, Namma Yatri allows auto-rickshaw drivers to retain 100% of the fare paid by passengers. This approach is intended to increase the earnings of drivers, who often struggle with high commission rates on other platforms.
Direct Driver-Passenger Connection
Namma Yatri facilitates a direct connection between auto-rickshaw drivers and passengers, bypassing intermediaries. This direct interaction eliminates the need for a third party to manage transactions, leading to more transparent fare structures and better communication between drivers and passengers. By removing intermediaries, Namma Yatri ensures that drivers have greater control over their work and earnings.
Government-Regulated Fares
The platform adheres strictly to government-regulated fare structures. Unlike other ride-hailing apps that may use dynamic or surge pricing, Namma Yatri’s pricing remains stable and fair, reflecting the rates set by local authorities. This regulation helps in maintaining transparency and prevents price inflation, ensuring that passengers are charged a fair rate for their rides.
Open-Source Technology
Namma Yatri is built on the Beckn Protocol, an open-source framework developed by the Beckn Foundation. This protocol allows for seamless, peer-to-peer connectivity between drivers and passengers. The use of open-source technology not only ensures transparency but also significantly reduces operational costs. By leveraging an open-source platform, Namma Yatri avoids the high costs associated with proprietary technology and allows for easier integration with other mobility solutions.
Community and Crowdfunding Support
To sustain its operations, Namma Yatri relies on community support and crowdfunding rather than traditional venture capital funding. This approach aligns with its mission to serve the community and maintain a low-cost structure. The platform invites contributions from users, drivers, and supporters who believe in its model and wish to see it thrive. This funding method not only supports operational costs but also reinforces the platform’s commitment to its core values of fairness and transparency.
Driver Empowerment
One of the standout features of Namma Yatri’s model is its focus on driver empowerment. By removing commission fees and providing a fair platform, Namma Yatri helps drivers achieve better financial stability. The platform offers tools and resources that enable drivers to manage their work schedules, track earnings, and connect directly with passengers, further enhancing their independence and job satisfaction.
Passenger Benefits
For passengers, Namma Yatri provides an affordable and transparent alternative to other ride-hailing services. With regulated fares and a straightforward pricing model, passengers can enjoy reliable transportation without the worry of unexpected surcharges. The platform’s user-friendly app ensures a smooth booking experience and fosters trust through its commitment to fair pricing and driver welfare.
Scalability and Expansion
The zero-commission and open-source nature of Namma Yatri’s business model also supports its scalability. As the platform grows and expands to other cities, the foundational principles of fairness and transparency can be easily replicated. The use of open-source technology and community support structures allows for a flexible and adaptable growth strategy, paving the way for future expansion and innovation.
Funding Update: Namma Yatri Raises $11 Million
Namma Yatri has recently secured $11 million in a significant funding round, spearheaded by Blume Ventures and Antler, along with contributions from other investors. This funding boost marks a pivotal moment for the platform, further validating its innovative approach to urban mobility and its commitment to driver empowerment.
The funding round saw participation from notable investors who recognize the potential of Namma Yatri’s zero-commission, driver-first model and its use of open-source technology. Blume Ventures, a leading venture capital firm known for supporting high-impact startups, and Antler, a global early-stage venture capital firm, both played key roles in this investment round. Their backing underscores the confidence in Namma Yatri’s mission and its ability to scale effectively.
Key Milestones Achieved
- Successful Launch: Namma Yatri made its debut in Bengaluru in 2022, quickly establishing itself as a viable alternative to traditional ride-hailing services. Its launch was marked by positive reception from both auto-rickshaw drivers and passengers.
- One Million Rides: Within its first year, Namma Yatri completed over 1 million rides, a testament to its growing popularity and acceptance among users.
- Partnerships with Auto-Rickshaw Unions: The platform secured crucial partnerships with local auto-rickshaw unions, including the Auto Rickshaw Drivers’ Union (ARDU), solidifying its position and gaining the trust of the driver community.
- Government Endorsement: Namma Yatri received backing from local government bodies for its adherence to regulated fares and its innovative approach to urban mobility.
- Expansion Announcements: Following its success in Bengaluru, Namma Yatri announced plans to expand to other major cities across India, aiming to replicate its successful model in new markets.
Challenges Faced
- Competition from Established Players: Competing with major ride-hailing companies like Uber and Ola, which have large user bases and extensive resources, has been a significant challenge. Namma Yatri has had to differentiate itself with its zero-commission model and community focus.
- Scaling Operations: Expanding to new cities presents logistical and operational challenges, including adapting to local regulations, integrating with new driver communities, and ensuring consistent service quality.
- Driver Onboarding: Convincing auto-rickshaw drivers to transition from established platforms with incentive schemes to a zero-commission model required substantial effort. Namma Yatri needed to demonstrate the benefits of its model and build trust within the driver community.
- Funding Constraints: Operating on a community-funded model limits immediate access to large capital investments. While this aligns with Namma Yatri’s values, it presents challenges in scaling quickly and investing in new technologies or features.
Future Plans
- Expansion to New Cities: Namma Yatri plans to expand its services to additional Indian cities, using its successful Bengaluru model as a blueprint for growth. The focus will be on establishing local partnerships and adapting to regional needs.
- Technological Enhancements: The platform aims to introduce new features and improvements, including advanced navigation tools, enhanced safety measures, and real-time ride tracking to further enhance the user experience.
- New Service Offerings: Namma Yatri is exploring the addition of new mobility services, such as bike rentals and micro-transit solutions, to broaden its service range and meet diverse transportation needs.
- Policy Advocacy: The platform will continue to advocate for open-source and driver-centric mobility solutions, working with policymakers and industry stakeholders to promote fair and sustainable practices in urban transport.
- Strengthening Community Support: Namma Yatri plans to deepen its engagement with the community through continued crowdfunding efforts and partnerships with social impact organizations, ensuring sustained support and alignment with its mission of transparency and empowerment.
In conclusion,
Namma Yatri stands as a pioneering force in the ride-hailing industry, demonstrating how a commitment to fairness, transparency, and driver empowerment can redefine urban mobility. By adopting a zero-commission model and leveraging open-source technology, Namma Yatri not only challenges the conventional norms of the ride-hailing market but also creates a more equitable ecosystem for both drivers and passengers. Its impressive milestones, including rapid adoption and expansion plans, underscore its potential to transform transportation in cities across India.
Despite facing challenges such as intense competition and scaling difficulties, Namma Yatri’s innovative approach and community-driven funding model provide a strong foundation for future growth. As the platform continues to expand and evolve, it remains dedicated to its core values of transparency and driver support, setting a new standard for how mobility solutions can operate in harmony with the needs of all stakeholders.

